Bitumen Application and Uses
Arteries Made with Asphalt
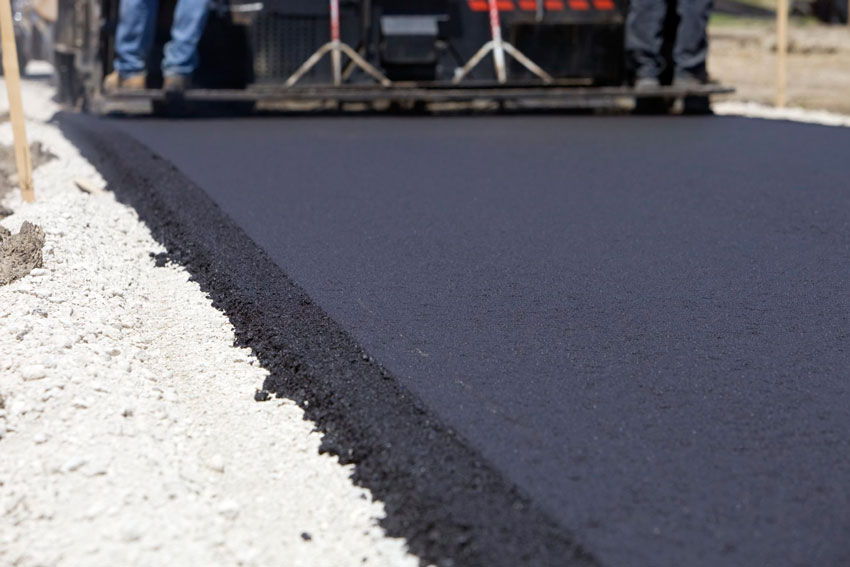
It is no surprise that most of our roads and streets are made of asphalt. Asphalt roads are more flexible to build and easier to maintain than roads using any other material. They are more cost-effective in both construction and maintenance and help reduce noise pollution. Asphalt roads are durable and are 100% recyclable. And asphalt is not just used in road surfaces: it is also a vital component of the substructure of the road, as well. And, of course, without bitumen, there would be no asphalt.
One recent advance has been the development of colored or textured asphalt surfaces. These can be used as a safety mechanism to make it easier for drivers to identify special lanes including bus lanes, bus stops, and cycle paths. Colored asphalt is also used to alert drivers to dangerous areas, such as hidden junctions or sharp bends, as well as areas requiring special safety precautions, such as outside schools.
Asphalt surfaces can be tailor-made to support the traffic load and climatic conditions of any location. There are asphalt solutions for motorways, urban, suburban and rural roads, and different solutions for high-load and bridge surfaces. In areas where roads are exposed to winter freezing and thawing, asphalt surfaces can be built to cope with extreme temperature differences, thanks to the flexibility of bitumen.
Asphalt roads can be constructed very quickly, and because asphalt effectively needs no “cure” time, motorists can use a new road soon after placement. Because of the way asphalt roads are built, they can be easily removed and resurfaced almost immediately. This is very important in urban environments where cables and pipes need to be laid or replaced under the street, as well as for general road maintenance, filling in potholes and even more so for our major trunk roads. Safe and smooth roads, with minimum delays.
Modern asphalts roads have shown to last for over 40 years and, with the correct maintenance, they can and do last even longer. Each road is built with a structurally solid base course and a protective, replaceable surface or wearing course. The layered structure is built to withstand traffic and the environment.
Modern asphalt technology ensures rapid drainage of surface water, reducing water spray and improving driver visibility in wet conditions. This reduces the risk of aquaplaning and increases the visibility of road markings. The surface texture ensures maximum grip and delivers optimal turning and braking performance, in all weather conditions. Asphalt surfaces that provide higher levels of skid resistance can be used where safety is paramount, for example on slip roads, junctions, and roundabouts.
Asphalt road surfaces can significantly reduce noise both inside and outside the car. Standard asphalt roads have the lowest noise levels of all traditional road surfaces and the most recent development of porous and silent asphalts have reduced noise levels even further. A standard asphalt surface produces half the noise compared to alternatives options such as concrete, and porous asphalt reduces this by a further 50%.
Asphalt is 100% recyclable and reusable. Recovered asphalt is routinely re-laid along with fresh materials, saving money and preserving non-renewable natural resources. Recycling also reduces the use of virgin quality gravel, reduces landfill and saves both cost and emissions for transport.
Shaping the World around us
The characteristics of bitumen give architects, structural engineers, and planners the freedom to redesign the world we live in. Bitumen membranes are water-repellent and flexible, making them ideal for waterproofing roofs and other structural elements. A natural adhesive, they can be applied to any number of substrate materials, and their natural flexibility helps to prevent rips and tears even with significant structural movement.
Bitumen membranes retain their adhesion and flexibility for a long time, and so can significantly contribute to a structure’s durability and longevity. Bituminous membranes have been used for decades and results show that a service life of 25-30 years can be expected in most applications.
Bitumen products are everywhere in modern buildings, in roofs and floors, ceilings and walls, both to protect the structural elements and to keep moisture out. Traditionally used to weatherproof low slope roofs, bituminous membranes are finding new uses in the movement towards carbon-neutral buildings. These membranes can be used to support roof gardens or eco-roofing, in both commercial and residential developments.
The correct surface is of vital importance in civil engineering projects: from bridges and tunnels to runways and parking aprons at airports. The surface needs to be strong enough to withstand each location’s different daily load and use patterns, as well as temperature differences, weather conditions and the use of aggressive de-icing technology. Bitumen products are designed to withstand the most extreme conditions and provide a safe, durable surface
Asphalt concrete with a void content of ≤ 3% is completely watertight and can be used to seal structures, basins or containers that will be used to contain water or other liquids. Asphalt can be used to waterproof dams, reservoirs, landfill sites and flood protection basins.
Part of our Everyday Life
This organic, versatile and recyclable material is never far away in the modern world – even if we don’t see it. Bitumen plays an important role in many everyday applications above and beyond asphalt streets and roofing. Bitumen’s waterproofing and adhesive properties, durability, and resistance to heavy loads make it the ideal material for use in all-weather environments. Where strength and weatherproofing are essential requirements, bitumen is a prime contributor to the performance of a vast range of products. Bitumen membranes are also extensively used as sound-deadening panels in the automobile market.
Farms use bituminous paints and disinfectants on a number of different surfaces as well as bitumen waterproofing solutions. Bitumen-based lubricants play a role in many industrial situations, and bitumen is a vital component in a range of products, from preservatives to plastics and sealants.
Modern farms rely on bitumen and products using refined bitumen for a number of vital applications. Bitumen paving provides flooring in barns, barnyards, and feed platforms while tanks, vats, and other concrete structures can be waterproofed with a bitumen solution.
Bitumen is everywhere – even in places where you wouldn’t expect to find it. It’s in a variety of grease and lubricant products for different applications, from the tracks of earth-moving equipment to traction motor gearboxes. It’s in corrosion-resistant paints and printing inks.
Bitumen is in the asphalt that paves perfectly smooth cycle paths and rugged, high-grip hiking trails, and much more. It is used to waterproof swimming pools and in numerous applications in event locations, from a huge stadium to a local playground. It’s the rubberized surface of running tracks and the waterproofing solutions used to treat outdoor clothing. In tennis courts and other sports surfaces.
BITUMEN recognized for its adhesive and cohesive assets, bitumen is often utilized in the construction industry. Bitumen is applied on road paving because it is viscous when hot, but solid once it cools down. Therefore Bitumen operates as the binder/glue for pieces of the aggregate.
The vast majority of refined bitumen is used in construction: primarily as a constituent of products used in paving and roofing applications. According to the requirements of the end use bitumen is produced to specification. This is achieved either by refining process or blending.
It is estimated that the current world use of bitumen is approximately 102 million tons per year. Approximately 85% of all the bitumen produced is used as the binder in asphalt for roads.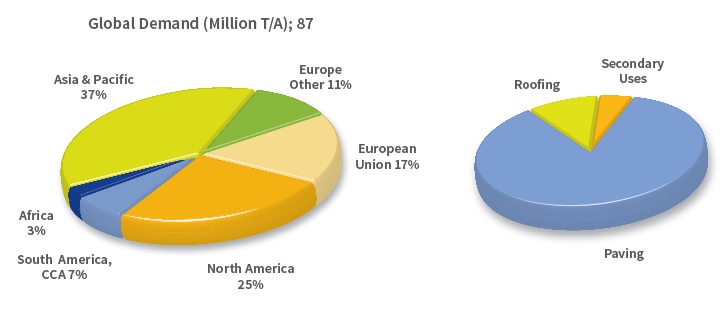
Bitumen is applied in construction and maintenance of:
Agriculture:
- Disinfectants
- Fence post coating,
- Mulches,
- Mulching paper Paved barn floors, barnyards, feed platforms
- Protecting tanks, vats
- Protection for concrete structures
- Tree paints (protective)
- Water And Moisture Barriers (Above And Below Ground)
- Wind And Water Erosion Control
- Weather Modification Areas
Buildings & industrial paving:
- Water & moisture barriers (above and below ground)
- Floor compositions, tiles, coverings
- Insulating fabrics, papers
- Step treads
- Building papers
- Caulking compounds
- Cement waterproofing compounds
- Glass wool compositions
- Insulating fabrics, felts, papers
- Joint filler compounds
- Laminated roofing shingles
- Liquid roof coatings
- Plastic cements
- Shingles
- Acoustical blocks, compositions, felts
- Bricks
- Dampproofing coatings, compositions
- Insulating board, fabrics, felts, paper
- Masonry coatings
- Plasterboards
- Putty
- Soundproofing
- Stucco base
- Wallboard
- Air-drying paints, varnishes
- Artificial timber
- Ebonised timber
- Insulating paints
- Plumbing, pipes
- Treated awnings
- Canal linings, sealants
Hydraulics & erosion control:
- Catchment areas, basins
- Dam groutings
- Dam linings, protection
- Dyke protection
- Ditch linings
- Drainage gutters, structures
- Embankment protection
- Groynes
- Jetties
- Levee protection
- Mattresses for levee & bank protection
- Membrane linings, waterproofing
- Reservoir linings
- Revetments
- Sand dune stabilization
- Sewage lagoons, oxidation ponds
- Swimming pools
- Waste ponds
- Water barriers
- Backed felts
Industrial:
- Conduit insulation, lamination
- Insulating boards
- Paint compositions
- Papers
- Pipe wrapping
- Insulating felts
- Panelboards
- Underseal
- Battery boxes, carbons
- Electrical insulating compounds, papers, tapes, wire coatings
- Junction box compound
- Moulded conduits
- Black grease
- Buffing compounds
- Cable splicing compound
- Embalming
- Etching compositions
- Extenders
- Explosives
- Lap cement
- Plasticisers
- Preservatives
- Printing inks
- Well drilling fluid
- Armored bituminised fabrics
- Burlap impregnation
- Mildew prevention
- Sawdust, cork, asphalt composition
- Acid-proof enamels, mastics, varnishes
- Acid-resistant coatings
- Air-drying paints, varnishes
- Anti-corrosive & anti-fouling paints
- Antioxidants & solvents
- Base for solvent compositions
- Baking & heat resistant enamels
- Boat deck sealing compound
- Lacquers japans
- Marine enamels
- Blasting fuses
- Briquette binders
- Burial vaults
- Casting moulds
- Clay articles
- Clay pigeons
- Expansion joints
- Flower pots
- Foundry cores
- Friction tape
- Gaskets
- Mirror backing
- Rubber molded compositions
- Shoe fillers, soles
Paving (see also agriculture, hydraulics, railways, recreation):
- Airport runways, taxiways, aprons
- Asphalt blocks
- Brick fillers
- Bridge deck, surfacing
- Crack fillers
- Floors for buildings, warehouses, garages
- Highways, roads, streets, shoulders
- Kerbs, gutters, drainage ditches
- Parking lots, driveways
- Portland cement concrete underseal
- Roof-deck parking
- Pavements, footpaths
- Soil stabilization
Railways :
Ballast treatment
Dust laying
Paved ballast, sub-ballast
Paved crossings, freight yards, station platforms
Recreation :
- Dance pavilions
- Drive-in movies
- Gymnasiums, sport arenas
- Playgrounds, school yards
- Race tracks
- Running tracks
- Skating rinks
- Swimming & wading pools
- Tennis courts, handball courts
- Synthetic playing fields & running track surfaces